Hypothesis testing
Welcome back to my 2nd last blog post for this module! The past week was so hectic and stressful with so many deadlines to meet and falling sick for about a week due to the rainy weather.
My group members from our Design of Experiment practical session were tasked to take on different roles of the Avengers, to allocate the runs that we will do hypothesis testing on, as shown below:
Yuhan : Iron Man (Run #1 & #3)
Joel: Thor (Run #2 & #4)
Myself : Captain America (Run #2 & #6)
Jian Ye : Black Widow (Run #4 & #8)
Jian Lun : Hulk (Run #3 & #8)
Hypothesis testing refers to the formal procedures used by experimenters or researchers to accept or reject statistical hypotheses.
The runs are allocated so that each of us will do hypothesis testing on
either the projectile weight or stop angle factor.
|
The QUESTION |
To determine the effect of stop angle on
the flying distance of the projectile |
|
Scope of the test |
The human
factor is assumed to be negligible. Therefore, different user will not have
any effect on the flying distance of projectile.
Flying distance
for catapult A is collected using the factors below: Arm length
= 33.1 cm Projectile
weight = 0.86 grams Stop angle = 50
degrees and 70 degrees
|
|
Step 1: State the statistical Hypotheses: |
State the null
hypothesis (H0): The distance travelled by the projectile remains unchanged when the stop angle increases from 50 degrees to 70 degrees while the arm length and the weight of the projectile are constant. State the
alternative hypothesis (H1): The distance travelled by the projectile reduces when the stop angle increases from 50 degrees to 70 degrees while the arm length and the weight of the projectile are constant. |
|
Step 2: Formulate an analysis plan. |
Sample size is 16 Therefore t-test will be used. Since the sign of H1 is “<”, a left tailed test is used. Significance level (α) used in this test is 0.05 (most commonly used)
|
|
Step 3: Calculate the test statistic |
State the mean
and standard deviation of Run #2: Mean = 145.3 Standard deviation = 4.43 State the mean
and standard deviation of Run #6: Mean = 114.9 Standard deviation
= 2.03
Compute the
value of the test statistic (t): Footnote 1
represents 50 degrees stop angle Footnote 2
represents 70 degrees stop angle x̄1 = 114.9 S1 = 2.03 x̄2 = 145.3 S2 = 4.43 n1 =
n2 = 8 V = n1 +
n2 -2 = 14 σ = (((8)(2.03)^2 + (8)(4.43)^2)/14)^0.5 σ = 3.6836 (4 d.p) t = (114.9 – 145.3)/(3.6836)((1/8) + (1/8)
)^0.5 t = -16.5 (3 s.f) |
|
Step 4: Make a decision based on result |
Type of test
(check one only) 1. Left-tailed
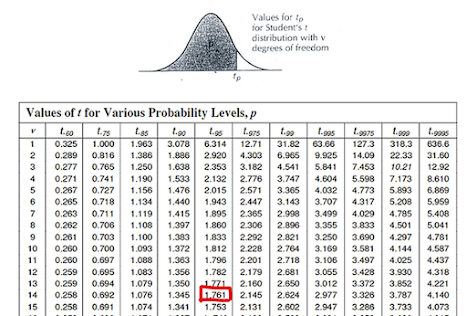
test: [✓] Critical
value tα = -1.761 2. Right-tailed test: [ __ ] Critical value tα =
______ 3. Two-tailed test: [ __ ] Critical value tα/2 = ± ______ Use the
t-distribution table to determine the critical value of tα or tα/2
Compare the values of test statistics, t (-16.5), and critical value(s), tα (-1.761) Therefore, Ho is false.
|
|
Conclusion that answer the initial question |
As H0 is false, H1 is accepted. This
indicates that the distance travelled by the projectile reduces when the stop
angle increases from 50 degrees to 70 degrees while the arm length and
projectile weight are constant.
|
|
Compare your conclusion with the conclusion from the other team
members.
|
Iron man and Thor reached the same conclusion that when the projectile weight is increased from 0.86g to 2.87g, the distance travelled by the projectile will decrease assuming no other factor is changed.
Captain
America and Black Widow reached the same conclusion that when the stop angle
increases from 50 degrees to 70 degrees, the distance travelled by the projectile
will decrease assuming no other factor is changed. |
|
What inferences can you make from these comparisons?
|
- Distance travelled by projectile decreases when the stop angle increases. - Distance travelled by projectile decreases when the projectile weight increases. |
|
Your learning reflection on this Hypothesis testing activity
|
Through my lessons and activities in Hypothesis Testing, I gained a deeper understanding of various concepts. For example, I learned the distinction between a statistical hypothesis and hypothesis testing. A statistical hypothesis is a supposition about a population parameter, which may or may not be accurate, while hypothesis testing refers to the systematic procedures utilized by researchers or experimenters to either accept or reject statistical hypotheses. I also gained knowledge of the steps involved in Hypothesis Testing and how to put them into practice. Additionally, through Hypothesis Testing, I discovered how factors such as arm length, projectile weight, and stopping angle impact the distance travelled by a projectile. In the future, I plan to apply what I have learned and utilize Hypothesis Testing to validate my conclusions. |




Comments
Post a Comment